Mikrotik now widely used by ISPs, hotspot providers, or by the owner of the cafe. Mikrotik OS router makes the computer into a reliable network that is equipped with various features and tools, for both wired and wireless.In this tutorial the author presents a discussion and a simple and simple instructions on configuring the proxy for certain purposes and the public is typically collected in server / router cafe as well as other tissues, such konfirugasi for example, for server NAT, Bridging, BW management, and MRTG.Mikrotik version I use for this tutorial is MikroTik RouterOS 2.9.27
Access Mikrotik:
1. via consoleMikrotik router board or PC can be accessed directly via the console / shell and remote access using putty (www.putty.nl)
2. via WinboxMikrotik can also be accessed / remotely using software tools Winbox
3. via webMikrotik can also be accessed via web / port 80 by using a browser
1. via consoleMikrotik router board or PC can be accessed directly via the console / shell and remote access using putty (www.putty.nl)
2. via WinboxMikrotik can also be accessed / remotely using software tools Winbox
3. via webMikrotik can also be accessed via web / port 80 by using a browser
Naming Mikrotik
[robby@ experiment > system identity print
name: "Mikrotik"
[robby@ experiment] > system identity edit
value-name: name
enter the editor type for example I change the name of the experiment:
IATG-SOLO
C-c quit C-o save&quit C-u undo C-k cut line C-y paste
Edit and then press Cltr-o to save and exit the editor.
Changing the name of the interface:
[robby@experiment] > /interface print
Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic, R - running
# NAME TYPE RX-RATE TX-RATE MTU
0 R ether1 ether 0 0 1500
1 R ether2 ether 0 0 1500
[robby@expriment] > /interface edit 0
value-name: name
The value 0 is the value ether1, if you want to replace ethet2 value 0 replaced by 1.go to my missal type editor replace with local names:
local
C-c quit C-o save&quit C-u undo C-k cut line C-y paste
Edit and then press Cltr-o to save and exit the editor Do the same for interfaces ether 2, so that if seen again will appear like this:
[robby@experiment] > /interface print
Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic, R - running
# NAME TYPE RX-RATE TX-RATE MTU
0 R local ether 0 0 1500
1 R public ether 0 0 1500
Via winbox:
Select the menu interface, click the name of the interface that wants to be edited, so it appears the edit window interface.
Seting IP Address :
[robby@experiment] > /ip address add
address: 192.168.1.1/24
interface: local
[robby@experiment] > /ip address print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 192.168.0.254/24 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 local
Enter the IP address value in the column address and netmask, enter the name of the interface that wants to be given ip addressnya.Untuk-2 Interface to the public interface, the same way as above, so that if seen again will be 2 interfaces:
[robby@experiment] > /ip address print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
# ADDRESS NETWORK BROADCAST INTERFACE
0 192.168.0.254/24 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 local
1 202.51.192.42/29 202.51.192.40 202.51.192.47 public
Via winbox:
As NAT Mikrotik
Network Address Translation or more commonly referred to as NAT is a method to connect more than one computer to the Internet network using a single IP address. Number of use of this method due to limited availability of IP addresses, the need for security (security), and the ease and flexibility in network administration.
Currently, the widely used IP protocol is IP version 4 (IPv4). With a length of the address 4 bytes means that there are 2 to the power 32 = 4,294,967,296 IP addresses available. This amount is theoretically the number of computers that can directly connect to the internet. Because of this limitation most of the ISPs (Internet Service Provider) will only allocate one address for one user and this address is dynamic, meaning that a given IP address will be different every time the user connects to the Internet. This will make it difficult for businesses to lower middle class. On the one hand they need more computers are connected to the Internet, but on the other hand only one IP address which means there is only one computer that can connect to the internet. This can be overcome by using NAT. By NAT gateways that run on one computer, one IP address can be shared with several other computer and they can connect to the internet simultaneously.
Suppose we want to hide the local network / LAN 192.168.0.0/24 202.51.192.42 behind one IP address provided by ISP, which we use is a feature of Mikrotik source network address translation (masquerading). Masquerading changes the data packets from the IP address and port from the network 192.168.0.0/24 to 202.51.192.42 henceforth be forwarded to the global Internet network.
To use masquerading, source NAT rule with action 'masquerade' should be added to the firewall configuration:
[robby@experiment] > /ip firewall nat add chain=srcnat
action=masquerade out-interface=public
As a transparent web proxy mikrotik
One function is to store the proxy cache. If a LAN uses a proxy to connect to the Internet, it is done by the browser when a user accesses a web server url is to take these requests on a proxy server. Whereas if the data is not contained in the proxy server then proxies to pick up directly from the web server. Then the request is stored in the cache proxy. Furthermore, if there are clients who make requests to the same url, it will be taken from the cache. This will make access to the Internet faster.
One function is to store the proxy cache. If a LAN uses a proxy to connect to the Internet, it is done by the browser when a user accesses a web server url is to take these requests on a proxy server. Whereas if the data is not contained in the proxy server then proxies to pick up directly from the web server. Then the request is stored in the cache proxy. Furthermore, if there are clients who make requests to the same url, it will be taken from the cache. This will make access to the Internet faster.
Enabling web proxy in mikrotik fiture:
[robby@experiment] > /ip proxy set enabled=yes
[robby@experiment] > /ip web-proxy set
cache-administrator= robby.ahmad@robby.net
[robby@experiment] > /ip web-proxy print
enabled: yes
src-address: 0.0.0.0
port: 3128
hostname: "experiment"
transparent-proxy: yes
parent-proxy: 0.0.0.0:0
cache-administrator: "robby.robby.net"
max-object-size: 8192KiB
cache-drive: system
max-cache-size: unlimited
max-ram-cache-size: unlimited
status: running
reserved-for-cache: 4733952KiB
reserved-for-ram-cache: 2048KiB
[robby@experiment] > /ip firewall nat add chain=dstnat in-interface=local src-address=192.168.0.0/24 protocol=tcp dst-port=80 action=redirect to-ports=3128
[robby@experiment] > /ip firewall nat print
Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic
0 chain=srcnat out-interface=public action=masquerade
1 chain=dstnat in-interface=local src-address=192.168.0.0/24 protocol=tcp dst-port=80 action=redirect to-ports=3128
In Winbox:
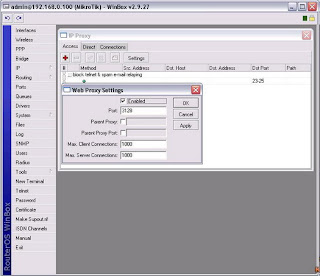
1. Enable web proxy on the menu IP> Proxy> Access> Settings (check box enabled)
2. Parameter settings on the IP menu> Web Proxy> Access Settings> General
3. Make a rule for transparent proxy on the menu IP> Firewall> NAT
Transparent proxy with proxy servers separate / independent
MikroTik Web Proxy built in according to my observations not so good compared to the squid proxy in linux, squid in linux has more flexibility to be modified and diconfigure, eg for delay-pool feature and ACL lists that include files, not in the proxy series 2.9.x.Usually most people prefer to create their own proxy servers, with PC Linux / FreeBSD and live directing all clients to the PC.Topology PC proxy can be in a local network or using public ip.Configuration almost similar to the transparent proxy, the difference is in the action NAT rule is as follows:
Mikrotik can also be used for bandwidth limiter (queue). To control the data rate allocation mechanism.In general there are 2 types of bandwidth management at the proxy, the simple queue and queue trees. Please use one onl
The next tutorial mikrotik all settings using Winbox, because it is more user friendly and efficient.
1.Settings on the menu Queues> Simple Queues
2.Click the ip> firewall> magle
3.Make a rule (click the + red) with the following parameters:
On the General tab:
Chain = forward,
Src.address = 192.168.0.3 (or who want to limit ip)
On the General tab:
Name = client3-up (eg),
Parent = local (as an interface into which direction),
Mark = client3 Package (choose from the dropdown, just that we make to magle)
Queue Type = default,
Priority = 8,
Max limit = 64k (for setting max upload bandwidth)
Click aplly and Ok
Src.address = 192.168.0.3 (or who want to limit ip)
Click Apply and OK
5. Create another rule with the following parameters:
On the General tab: chain = forward
Connection mark = client3-con (choose from dropdown menu)
On the Action tab:
Action = mark-packet,
New pcket Mark = client3 (or the name of the packet we created a distinguished mark)
Click Apply and OK
On the Action tab:
Action = mark-packet,
New pcket Mark = client3 (or the name of the packet we created a distinguished mark)
Click Apply and OK
6. Klik menu Queues>Queues Tree
Make a rule (click the + red) with the following parameters: On the General tab
Name = client3-in (eg),
Parent = public (which is the direction of outgoing interface),
Mark = client3 Package (choose from the dropdown, just that we make to magle)
Queue Type = default,
Priority = 8,
Max limit = 64k (for setting the bandwidth max download)
Click aplly and Ok
Create another rule with the following parameters:
Parent = public (which is the direction of outgoing interface),
Mark = client3 Package (choose from the dropdown, just that we make to magle)
Queue Type = default,
Priority = 8,
Max limit = 64k (for setting the bandwidth max download)
Click aplly and Ok
Create another rule with the following parameters:
On the General tab:
Name = client3-up (eg),
Parent = local (as an interface into which direction),
Mark = client3 Package (choose from the dropdown, just that we make to magle)
Queue Type = default,
Priority = 8,
Max limit = 64k (for setting max upload bandwidth)
Click aplly and Ok
Similarly, the authors convey a little tutorial for just sharing the knowledge or simplify for easy understanding of the tutorials that are already available on the official site mikrotik.




Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar